 Abstract: Infectious diseases are very common in our country as well as other developing countries and it accounts about 50% of all diseases. Antimicrobial agents are very helpful in reducing the global burden of infectious diseases. Now days, drug resistance to human pathogenic bacteria has been reported from every part of the world.
Abstract: Infectious diseases are very common in our country as well as other developing countries and it accounts about 50% of all diseases. Antimicrobial agents are very helpful in reducing the global burden of infectious diseases. Now days, drug resistance to human pathogenic bacteria has been reported from every part of the world.
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate antibacterial activity of Mercurius solubilis in all potencies in vitro for their activity against staphylococcus aureus isolates.
Materials and Methods: Nutrient broth media for bacterial growth was used and then Mercurius solubilis was added to evaluate the percentage of inhibition according to turbidity in all test tubes.
Result: All potencies showed inhibition of Staph. A. But, it was found that 10M of Mercurius solubilis is more effective for Staph. A growth inhibition.
Introduction
For the past 200 years or so we are the preferred target for material existence, proof, recognition and modus operandi of Homeopathy. There are some areas where we lack or are being criticized. It is a heartfelt need to strengthen our science as per the scientific methods applied universally. This is the fundamental challenge in front of us now, so we must explore the hidden areas, define the flaws and open new horizons for future research. The main aim of research is to look into the matter in a scientific and rational attitude and the conclusions and benefits must be used for the development of skills, clinical practices and repertories.
Now days infectious diseases are very common in our country as well as other developing countries and it accounts about 50% of all diseases. Antimicrobial agents are very helpful in reducing the global burden of infectious diseases. Drug resistance to human pathogenic bacteria has been reported from every part of the world. Therefore, there is a high need to discover and develop new method for combating microbial infectious diseases caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
In today’s world homoeopathy medicines are proved to cure almost all type of illness. So, it can also be tried to combat bacteria. Staphylococcal infections are the most common bacterial infections, especially in hospitals. Some common staphylococcal infections are folliculitis, abscess, wound infection, carbuncle, osteomylitis, pyomyocitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, etc.
In Homeopathic Materia Medica and Repertories, Mercurius solubilis is described as a great remedy for suppurative conditions. Mercurius solubilis has been selected for research to see whether it can kill staphylococcus aureus or inhibit the growth.
Materials and Method
Study settings: The study was done in (in vitro) microbiology laboratory of Rajiv Gandhi institute of IT and Biotechnology, Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune- 46.
Media and chemicals: All media was procured from Hi Media Mumbai, India. All the reagents and chemicals used in this work were of AR grade and procured from MERK India.
Homoeopathic Drug preparation: Homoeopathic drug Mercurius solubilis in 6CH, 12CH,30 CH, 200 CH, 1M, 10M, 50M, with their liquid dilutions were obtained from Dr. Willmar Schwabe India Pvt. Ltd.
Organism: Staphylococcus aureus (NCIM) was used as standard culture to examine antimicrobial activity. Other culture used in this study is clinical isolates procured from Bharati Hospital, Pune.
Antimicrobial assay: Antimicrobial assays was performed using L-B (Luria Broth) medium or Mueller Hinton agar. For this the isolates and reference cultures was grow in LB medium to McFarland standard 0.5 for 1.5 approximate cell density of culture was spread individually on LB or Mueller Hinton plate containing base agar overplayed with soft agar.
The well was punctured in soft agar at equidistance using 3-5 mm bore. Drug potencies used for testing were 6CH, 12CH 30CH, 200CH, 1M, 10M, 50M. Only solvent in one well on each plate is ethanol which serves as control.
Plates were incubated at 37-degree C for 24 hours. At the end of incubation period diameter of zones of inhibition was measured.
But, in plate the zone of inhibition is not measurable because it is not present uniformly or present in zigzag manner. (See Figure 1) So, nutrient broth media was chosen over agar plates.
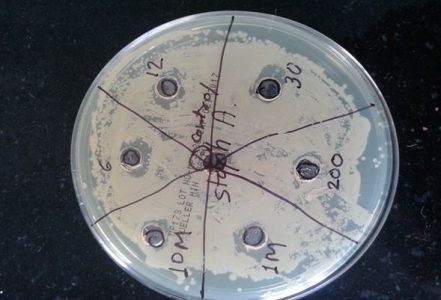
Figure 1: Plate method
Exclusion criteria
Following subjects are excluding in the study
- Infected material of patient suffering from sexually transmitted disease like HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, Kaposi sarcoma etc.
- Patient having malignancy from any origin.
Inclusion criteria
Samples collected from patient of different age group including male, female and children.
Outcome assessment
It was reported as sensitive, moderately sensitive, or resistant, referring to the Kirby-Bauer chart reading.
Statistical techniques
Statistical techniques and methods were used wherever required accordingly.
Data analysis: Data analysis was done after the result of experiment.
Dilution Method
- The experiment was done with 10 drops of medicine, 20 drops and 30 drops of homoeopathic medicine with all potencies.
- Fresh culture was prepared from previously isolated culture of Staphylococcus aureus in nutrient broth.
- Preparation of nutrient broth media for dilution method. 8.5 ml in each test tube.
- Autoclaved all test tube, distilled water, micro tips and prepared media for 15 minutes on pressure 15 PSI (pounds per square inch absolute) at 1200
- After autoclave allowed all test tubes to be cooled and then labelled the test tube like- positive control, negative control, and alcohol control (90%) and test control 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 etc. according to their respective potencies.
- Added 0.5ml freshly prepared culture of Staphylococcus aureus in all test tubes except negative control.
- Add 20ml of autoclaved distilled water in positive and negative control.
- Add 20ml of 90% alcohol to alcohol controlled test tube.
- After that we added 20 drops of homoeopathic medicine Mercurius solubilis of each potency in respective test control test tubes.
- Then allowed all test tubes for incubation for 24hrs to see the sensitivity of bacteria to either alcohol or medicine or compare it.
Result and Observation
In-vitro growth of staphylococcus aureus exhibited significant reduction in the presence of Mercurius solubilis 6c 12c 30c 200c 1M 10M 50M compared to negative test and control (90%alcohol). The best result was best obtained by 10M potency which inhibited the maximum bacterial growth or showed less turbidity as compared to other potencies.
Effects of Mercurius solubilis on Staphylococcus aureus
- Finally, the graph shows Mercurius solubilis 10M and 30C inhibited maximum number of growth of staphylococcus aureus.
- Mercurius solubilis 12C showed minimum growth inhibition.
Discussion
Resistance of the bacteria to the antibiotics is the major health problem all over the world. So it is necessary to discover new and effective mode of treatment which is able to combat resistant bacteria. In the study, the action of homoeopathic medicine Mercurius solubilis was investigated in different potency on thirty cultures of Staphylococcus aureus for twenty-four hours.
In all thirty samples and seven potencies, the best results were found in Mercurius solubilis 30c and 10 M potency which covers 16 samples in which the growth of staphylococcus aureus was inhibited or showed less turbidity, that is compared to negative test and control test with 90 % alcohol.
Conclusion
Homoeopathic medicines used in infectious conditions does not work as an antibiotic. They do not directly kill bacteria but they inhibit the growth of the bacteria. In homoeopathic system of medicine, the medicine stimulates defense mechanism of the host.
For more authenticity the experiment should be done on micro titre plate to see the number of bacterial growth.
Acknowledgement
Prof. Dr. Arun B. Jadhav Principal of Bharati Vidyapeeth Homeopathic Medical College Pune. and Dr. Rama Bhadekar (PhD Microbiology) Head of department of microbiology, of Rajiv Gandhi institute of IT and Biotechnology, Bharati Vidyapeeth Deemed University, Pune is thankfully acknowledged for supporting the work in the department.





