Abstract : Nowadays, the community commonly shows the symptoms ofSycotic Miasm. Clinically it affects any part or system of the body like UterineFibroids, Ovarian Cysts, PCOD, Asthma, Warts, Eczema, Psoriasis, Calculi Like (Renal Calculi, Gall Bladder Calculi Or Salivary Gland Calculi),Calcaneal spur etc.
Here I present a short introduction of Salivary calculi i.e. Sialolithiasis with a Case which shows many Sycotic presentations in the same case and also tried to explain a relationship of remedies in followup as a second prescription.
Key words : Sialolith, salivary glands, salivary calculi, Sycotic Miasm, Hekla lava, Merc sol, Iodum, drainage remedy, surgical case and homoeopathy.
The salivary glands are exocrine glands that make, modify and secrete Saliva into the oral cavity.
Types
They are divided into two main types:
- The major salivary glands- Parotid gland, Submandibular gland and Sublingual glands.
- The minor salivary glands- Labial, Buccal, Palatine and Lingual glands- numerous in numbers.
PAROTID GLAND: It is located around the Ear, between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the masseter muscle.
Stensen’s duct, the main excretory duct of the parotid gland, projects from the anterior border of the gland. It pierces the buccinator muscle to open into the oral cavity at the opposite of the buccal mucosa of the upper second molar tooth.
SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND:The submandibular gland (SMG) is the second-largest gland. It is found inferior to the mandible, between the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle.
Wharton’s duct, the main excretory duct, arises from the smaller, deep lobe inferior to the mucosa of the floor of the mouth to enter the oral cavity. It opens into the frenulum linguae at the sublingual region. The hypoglossal nerve runs parallel and inferior to Wharton’s duct.
SUBLINGUAL GLAND:The sublingual gland (SLG) lies beneath the mucosa of the floor of the mouth and superior to the mylohyoid muscle. Rather than having one main duct, it contains a series of short ducts that project directly into the floor of the mouth, the ducts of Rivinus, and a common duct, known as Bartholin’s duct that connects with the submandibular gland’s duct at the sublingual region.
Human salivary glands produce between 0.5 to 1.5 L of saliva daily. It facilitating mastication, swallowing speech, lubricating the oral mucosa and providing an aqueous medium for taste perception. They also participate in the digestion of triglycerides and starches by secreting lipases and amylases enzyme. In addition, saliva plays a protective role against infections via its many organic constituents.
SALIVARY CALCULI / SIALOLITHIASIS
- Sialoliths are calcified structures that develop within the salivary gland or the ductal system.
- Men > Women, Rare in children.
- Submandibular Gland: Very common, 80-92% and larger and intraductal.
- Parotid Gland: 6-20% and multiple within the gland.
- Sublingual and other Minor Salivary Glands: 1-2%
Sialoliths are common in SUBMANDIBULAR GLAND due to:
- Abundant calcium concentration- Calcium carbonate & calcium
Phosphate
- Alkaline pH.
- Wharton’s duct: longest, two sharp curves and small punctum.
Pathogenesis: Sialoliths form due to secretory disturbances & precipitation due to inflammation.
Metabolic disturbances as in alkalinity and precipitation.
Progression:
Secretory disturbances cause viscous secretions.
Microlith formation causes ductal obstruction.
Symptoms:
- Pain, swelling & discomfort.
- Pain severe during meal time with sweet, sour or acidic food.
- Unusual taste.
- If associated with infection- Fever, Purulent Discharge And Lymphadenopathy.
Histology: Stratified & mineralized with metaplastic excretory duct cells
- Concentric laminated structures
- Acini infiltrated by lymphocytes
- Dilatation of duct
- Epithelium exfoliation
Diagnosis:
- History
- Clinical examination: Bi-manual palpation
- Imaging
Treatment :
- Extracorporeal Short-Wave Lithotripsy And Sialo-endoscopy are effective alternatives to conventional surgical excision for smaller sialoliths.
- Trans-oral sialolithotomy with sialodochoplasty or sialoadenectomy- for giant sialoliths.
Homoepathic Treatment: Merc Sol, Calcarea Carb, Calcarea flur, Conium Mac, Baryta Carb, Iodum, Ars Iod, Silicea, Thuja, Hekla lava, Lapis Albus
CASE:
- A female Patient aged 40 years complaining of pain at the floor of the mouth which is radiating towards the ear back to the lobule since 8-10 days. Swelling at the floor of the mouth on the right side of the frenulum. Profuse salivation. No fever. Pain aggravated during and after eating and on touch, amelioration in empty mouth. Took antibiotics for 5 days but no relief.
- Patient narrated that the feeling of sand like particle at the floor of the mouth on the right side of frenulum.
- She was on the homoeopathic treatment for Asthma and fibroids since last 1 year.
- On Thyrox 75 (doses fluctuating as per values of TSH)
- Patient is a known case of asthma since childhood, Migraine since 20 years,Hypothyroidism since 14 years, uterine small multiple fibroids since 8 years, Cyst on the forehead, wart on right gluteal region (1*1.5cm) and on labia majora, eczema on leg.
Family History:
- Mother– Asthma, Diabetes Mellitus, Hypertension, Osteoarthritis, Hysterectomy for Fibroids, Fatty Liver.
- Father – Hypertension, Asthma, Died due to cardiac arrest at the age of 48 years.
- Sister– Multiple Fibroids in Uterus. Operated Right Ovarian Cyst.
- Brother– Hypertension, Cervical Spondylosis, Arthritis, MI attack.
Personal History:
- Diet: Veg & Non veg
- Appetite: Reduced since complaints
- Desire: Sweet, eggs+++
- Aversion: Sour
- Thirst: Increased
- Elimination:
Urine: Normal
Stool: sometimes constipated
Perspiration : Profuse
On Examination:
Floor of the mouth– congested and inflamed. Swelling on the right side of the face from below the angle of the mandible to the ear. Submandibular group of Lymphnodes enlarged slightly and was painful. Small whitish projection at the floor of mouth just right to the frenulum, Halitosis.
Diagnosis: Sialolithiasis of Submandibular gland duct.
Dominant Miasm: Sycotic Miasm.
Prescription:
Merc sol 30, HS x 3 days (Profuse Salivation, halitosis & pain)
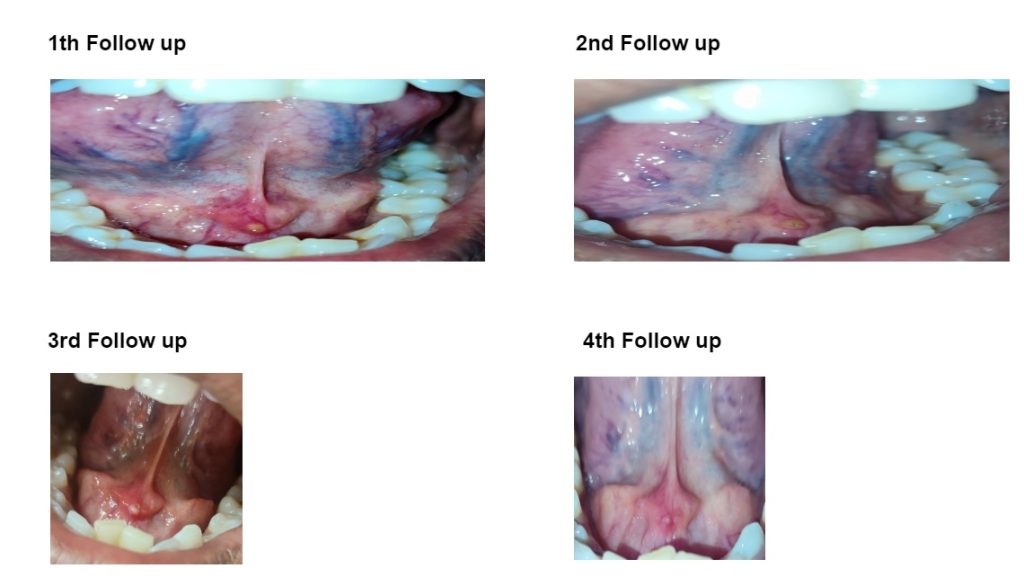
1st Follow up after 8 days: Sialolith clearly appearing.
Decrease salivation & Halitosis, pain same.
2ndPrescription –
Iodum 6c BD * 3days (Drainage remedy)
Calcarea carb 200 Stat
SL BD *10days (* Calc.carb & Iod follows well to merc sol)
2nd Follow up after 12 days: Stone becomes very superficial and tries to come out, very painful.
Hekla lava 1M OD alternate day- 3 doses (*silicea is inimical to Merc sol, so it is not prescribed)
SL BD* 7days
3rd Follow up (on call) after 6 days : Stone comes out during Brushing the teeth at morning
4th Follow up after 2 days : Inflammation at floor of mouth completely reduced.
Conclusion : Sialolithiasis is a surgical disease. But with due respect to the patient and her family towards Homoeopathy, did not wish to take surgical intervention and wanted a homoeopathic line of treatment. Here, again Homoeopathy line of treatment proves its scientificity. With the help of Constitutional medicine, drainage remedy and Hekla- lava patient gets completely cured her salivary calculi. Here Homoeopathy shows rapid, gentle and permanent cure and surgery gets avoided.
(Note: constitutionally the patient was Calcarea carb. She is known to have many glandular affections so Iodum 6c is given as a drainage remedy. Hekla lava is given for excision like lava.)