ABSTRACT
Kidney failure has been ascribed as the end-stage renal disease. It is the last stage of chronic kidney disease. At this juncture of case search for alternative medicines becomes necessity. In homoeopathic materia medica, there are wide ranges of rare medicines. Eel serum has earned much popularity among the homoeopathic practitioners as therapeutics application on specific basis. The serum of the eel has a toxic action on the blood, rapidly destroying its globules. The presence of albumin and renal elements in the urine, the haemoglobinuria, the prolonged anuria (24 and 26 hours), together with the results of the autopsy, plainly demonstrate its elective action on the kidneys. Secondly, the liver and the heart are affected, and the alterations observed are those usually present in infectious diseases.
KEYWORDS
Kidney failure, Eel serum.
ABBREVIATIONS
ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide), VNP (ventricular natriuretic peptide).
INTRODUCTION
Eel serum, or Serum anguillae, or Ichthyotoxin, is a constitutional remedy or organ remedy or renal remedy as indicated in cases of renal failure. But simultaneously, it is one of our most neglected remedies. It is neither mentioned in Kent’s nor in Clarke’s materia medica. Fresh water Eel is a sea remedy, and its toxic action is noted in the ninth edition of Boericke’s Materia Medica, where it is stated that the serum of eel destroys blood globules and has an elective action on the kidneys. Not much has been known about this remedy, except the fact that it is routinely prescribed for renal failure with infrequent results especially in low potency.[1]
The fact is that kidney has an important role in the maintenance of internal environment of the human beings. Its primary function is homoeostasis (maintenance of electrolyte balance). It maintains blood pressure, blood calcium level, water, etc.
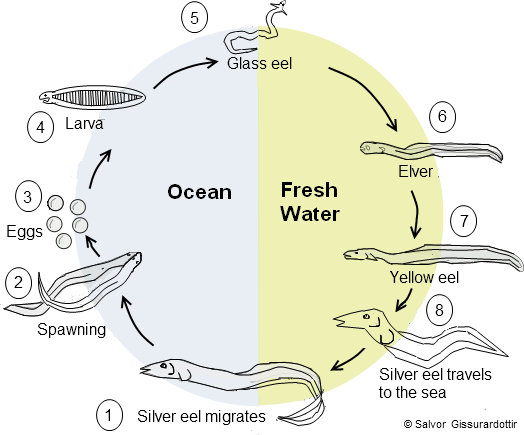
Eel is a very interesting type of fish. It has unique mechanism of reproduction for which it migrates for spawning from fresh water to seawater. For this migration, it undergoes metamorphosis or certain adaptation to maintain the hypertonic and hypotonic environment, which resembles the features like kidney. Renal pathology also runs so far as like eel migration and finally tired of the advanced pathology, the patient gives up with the failure of kidney functions. This is the key point which indicates the use of Eel serum for renal pathology.
Eel resemble like underwater snake so it has attack and defense mechanism which is a strong animal feature; other feature like if one tries to catch the eel fish with a bit of wool tied round a hook, it will avoid for they are terrified of choking, and they hate constriction. If you stand on the tail of a wriggling eel it will die. This resembles with Lachesis mutus in the throat complaints where the sensitivity of the throat to touch and constriction is seen.[2] For spawning, it travels so far which indicates the symptoms of travelling desire in this medicine. They are not very colourful, or attractive but they do have a strange beauty of their own with slippery or sleathery skin. The luminance in the body which is seen when it moves with water current is mesmerising to watch. Several things about eel make them unique; they are interesting not only ecologically but also because of their unique biography. This character which is not found in any other animal in this planet, that it has catadromous life cycle. Some of the specimens do not migrate and pass their entire life cycle in the sea, without ever migrating towards fresh waters. Eel blood is toxic to the humans and other mammals but both cooking and the digestive process destroy the toxic protein. The toxin derived from eel blood serum was used by Charles Robert Richard in his Nobel prize-winning research that discovered anaphylaxis (by injecting it into dogs and observing the effect). Apart from that in 2010, Greenpeace International has added the European Eel, Japnese Eel, and American Eel to its sea food red list.[3]
The keynote of the Eel serum remedy is acute anuria, oliguria and albuminuria, in renal failure with high creatinine, without oedema. Clinically, acute (or subacute) kidney inflammation (frigor–cold, infection or intoxification) is seen with albuminuria, ischuria, uraemia or even anuria. Later on heart or liver affections are seen; or during heart disease, sudden acute kidney involvement may be noted. It has marvellous effect in severe hypertensive cases.
Heart trouble secondary to renal mischief with functional disturbance like systolic insufficiency (asystolia), decompensation, valvular (mitral) incompetency, dyspnoea (emphysema), oedema(or more) may be noticed. With some definite renal symptoms, oliguria (preparatory for renal failure), and uraemia and in addition hepatomegaly is seen. [4] Donald Gladwish writes that eel’s serum (serum anguillare ichthyotoxin) was very useful in hypertension with renal diseases, presenting no guiding symptom.[5]
REVIEW OF LITERATURE
NATURE OF EEL Eel belonges to the:
Kingdom – Animalia,
Phylum – Chordata,
Class- Actinopterygii,
Sub-order – Elopomorpha,
Zoological name: Anguilla rostrata Le Sueur.
Synonyms: Latin: Ichthyotoxinum, Serum anguillae ichthyotoxinum; English: Eel serum; French: Serum d’anguille.
Uses: Heart and kidney disease, failure of compensation and impending a systole.
Parts used: The serum.
An eel is any ray finned fish belonging to the order Anguilliformes, which consists of eight suborders, 19 families, 111 genera, and about 800 species. Eels are elongated fish ranging in length from 5cm in one jaw eel to 4m in the slender giant moray. Adults range in weight from 30gm to 25kg. The fresh water eels are widely distributed in all over the world.
Most of the eels live in shallow water of the ocean and burrow into sand, mud, or amongst rocks. Only members of Anguilla live in fresh water but they too return to the sea to breed. European eel migrate to the sargasso sea for reproduction. Eel breathe through skin. The reason for migration in the eel is still a mystery and when they migrate they completely disappear from the human view, no one has witnessed or unable to follow their migration. They don’t return to the fresh water again and it is assumed that after completing long and mysterious journey they finally die in the same place where they were born. But why they travel so far is still a mystery. It was observed while analysing the ratio of strontium and calcium in the otoliths (earstones) of the eels. Fresh water has little strontium with respect to sea water, and its concentration in otoliths reflects the time which single individuals spend in marine or fresh water habitats.[6]
DESCRIPTION
The toxic serum of the wel (Anguilla rostrata Le Sueur),
a ray-finned fish with a long, slender, snake-like body, laterally compressed
at the posterior end, and reaching a length of 0.6 m. The scales are minute and
embedded in the yellowish-brown skin, thus giving it a smooth appearance. The
eel is a catadromous fish, spending most of its life in fresh water, and moving
to the ocean to spawn. Eel serum is a yellowish to greenish-yellow, opalescent
liquid; it may be pink due to a slight haemolysis.
Distribution: Occupies most of the rivers d eastern North America from the
southern Great Plains to the Atlantic Coast, from southern Greenland and
Labrador to northern South America, and in the Missippi Valley as far north as
Minnesota and South America. The mature adults are found in the vicinity d
Bermuda, where spawning occurs.
Preparation: Carry out under strict condition of cleanliness. Select
vigorous healthy eels weighing about 1 kg. Immobilize the eel on its back, and
with a scalpel dissect the abdominal wall for a 10-12 cm length from the gills.
Expose the branchial artery, separate it from surrounding tissues and clamp it.
Place sterile centrifugation tube against the artery and cut the artery above
the tube. Collect the blood freely by using abdominal massage. Stop the tube,
allow it to stand for 1-2 hours at room temperature, centrifuge at 5,000 r. p.
m. for 15 min. and decant the serum. Pure eel serum should not be stored, and
attenuations up to 3X (1X1000) should be prepared without delay, with
isotonic sodium chloride solution.[7]
Life cycle
Eel have unique characters such as a catadromous life history strategy, a long spawning migaration, and a long leptocephalus larval period. Bisexuality seen in Eel, when they live in fresh water they are male (blackish and more pigmented), but when they move to sea become 2-3 times bigger than future male. Eels undergo considerable development from the early larval stage to the eventually adult stage. Eels swim by generating body waves which travel the length of their bodies. They can swim backwards by reversing the direction of the wave. When they move from fresh water to sea water they undergo metamorphosis. Eyes enlarge by 10 times, skin get thicker and fins get larger.
Multicellular complexes of chloride cell which is of two types filament and lamella, were observed in the integument of the body surface function as major osmo-ionoregulatory sites, at least until early leptocephalus stage. Chloride cell complexes found found in salt water eel and rarely observed in fresh water eel. Formation of the complexes is related to the salt water adaptation and are important for salt secretion in hypertonic environment, this salt secretion resemble with the salt desire of Eel serum. Towards the downstream migration of the eel to sea, the ratio of filament chloride cells increases and concomitant decrease in the lamella chloride cell.[8]
DEFENSE MECHANISM
Plasma of the eel has highly haemolytic activity against the heterogenous erythrocytes. The defence mechanism is characterised by specific antibody acquired by the antigen stimulation, usually by infection. Eel has Immunoglobulin M antibody.
BIOCHEMISTRY
Eel has three hormones (all are natriuretic peptides). These are ANP (atrial natriuretic peptide) from atria, VNP (ventricular natriuretic peptide) from ventricles, and C-type natriuretic peptides from brains. All three harmones were circulating in the eel blood, and there plasma level invariably decreased when eels were transferred from fresh water to sea water. Eel ANP and VNP inhibited drinking in fresh water and sea water eels. Eel ANP inhibited water and Na+ absorption by the intestine of sea water eels. Eel ANP and VNP induced antidiuresis but not antinatriuresis in fresh water eels. Eel ANP increased plasma cortisol level in sea water eels but not in fresh water eels. Thus ANP plays a complex role in the eel osmoregulation. These mechanism is used for the effective treatment in renal pathology.[9]
Dr Boericke has beautifully explained that serum of eel (Eel serum), has a toxic effect on the blood, rapidly destroying its globules. The presence of albumin and renal elements in urine, hemoglobinuria, prolonged anuria (24-26hours), together with the results of autopsy, plainly demonstrate its elective action on kidneys. A priori, therapeutical indications of Eel serum is whenever the kidney is acutely affected, either from cold, infection or intoxification, the attack is characterized by oliguria, anuria, and albuminuria , we will find Eel’s serum eminently efficacious to re-establish dieresis, and it rapidly arrests albuminuria. Serum of eel seems better adapted to cases of hypertension and oliguria without oedema . Serum of Eel has has put an end to the renal obstruction and produced an abundant diuresis. But it is really specific indication seems to be for acute nephritis a frigori (jousset).[10]
Dr Nels Bergman of Chicagoused Eel serum in in low potency in hypertension and kidney disease.[11] Chiron reports a case of congestive heart failure cured by Eel’s serum.
Eel serum: its action is more on the kidneys than on the heart. The pathology was studied by Pierre Jousset in hospital saint Jacques. Late Dr Picard, who also belonged to same hospital saint Jacques, has also done some remarkable studies on the serum of eel, and in the congress of Budapest in 193, he presented an extremely interesting report on this remedy. Serum of eel in 3x is an excellent remedy for acute nephritis.[12]
SOME IMPORTANT INDICATION OF EEL’S SERUM SYMPTOMS
- POSTPONING everything to next day constant postponing and wanting to avoid daily routine, kind of aversion towards doing everything.
- There is a kind of discontended, low, irritable indifference towards their work.
- Tendency to make fun about horrible things.
- Pains wander from toes to knees and hips, and from fingers to elbow and shoulders.
- Nausea concomitant of heart and kidney diseases.
- Desire for salt, sweet, coffee.
RUBRIC RELATED TO EEL SERUM
MIND – AILMENTS FROM – domination
MIND – AILMENTS FROM – domination – children; in
MIND – AILMENTS FROM – domination – children; in
– parental control; long history of excessive
MIND – MYSTICISM
POSTPONING everything to next day
DISCONTENDED; work, with his
IRRITABILITY; work, about
DREAMS; amorous (358)
DREAMS; animals, of (332)
DREAMS; exciting, (33)
DREAMS; journey, travlling (140)
DREAMS; many, (315)
DREAMS; snakes, (87)
DREAMS; snakes; black with yellow design (1)
DREAMS; storms (26)
DREAMS; vivid (271)
DREAMS; water, (219)
DREAMS; water; flood, of a (45)
JESTING; (101)
JESTING; puns, makes (4)
KICKS; (50)
KICKS; tantrum, in (6)
ABDOMEN – LIVER AND REGION OF LIVER; COMPLAINTS OF
BLADDER – RETENTION OF URINE
KIDNEYS – COMPLAINTS OF KIDNEYS
KIDNEYS – INFLAMMATION
KIDNEYS – INFLAMMATION – acute
KIDNEYS – INFLAMMATION – parenchymatous
KIDNEYS – INFLAMMATION – subacute
KIDNEYS – PAIN – cold; exposure to
KIDNEYS – RENAL FAILURE
KIDNEYS – RENAL FAILURE – chronic
KIDNEYS – SUPPRESSION OF URINE
URINE – ALBUMINOUS
URINE – BLOODY
URINE – CASTS, CONTAINING
URINE – SCANTY
RESPIRATION – DIFFICULT
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – accompanied by – respiration – difficult
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – accompanied by – uremia
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – accompanied by – urine – scanty
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – accompanied by – Kidneys – complaints
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – edema – without
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – mitral regurgitation
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – tricuspid regurgitation
CHEST – HEART; COMPLAINTS OF THE – Valves
CHEST – HEART FAILURE
CHEST – HEART FAILURE – Mitral valve
CHEST – MILK – decreased
CHEST – PALPITATION OF HEART
CHEST – PALPITATION OF HEART – irregular
CHEST – SWELLING
CHEST – SWELLING – Mammae
CHEST – SWELLING – Mammae – edematous
CHEST – SWELLING – Mammae – edematous – delivery; during first
CHEST – WEAKNESS
CHEST – WEAKNESS – Heart
CHEST – WEAKNESS – Heart – accompanied by – dropsy
EXTREMITIES – SWELLING
EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – Legs
EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – Legs – lymphatic swelling
EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – Lower limbs
EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – Lower limbs – injuries; after – lymphatics; of the
GENERALS – BLOOD – degradation
GENERALS – DIABETES MELLITUS
GENERALS – DROPSY – external dropsy
GENERALS – DROPSY – external dropsy – heart disease; from
GENERALS – FOOD AND DRINKS – coffee – desire
GENERALS – FOOD AND DRINKS – pungent things – desire
GENERALS – FOOD AND DRINKS – salt – desire
GENERALS – FOOD AND DRINKS – sweets – desire
GENERALS – HYPERTENSION
GENERALS – HYPERTENSION – dialysis; from
GENERALS – INFECTIOUS DISEASE
GENERALS – LABORATORY FINDINGS – creatinine – increased
GENERALS – PULSE – fluttering
GENERALS – PULSE – frequent
GENERALS – PULSE – imperceptible – almost
GENERALS – PULSE – irregular
GENERALS – PULSE – weak
GENERALS – UREMIA[13]
REFERENCES
[1] British Homoeopathic journal – Article on Eel or serum Anguillae Icthyotoxin by A.C.G Gross ; volume 68, Issue4, October 1979, pages 227-229 [2] British Homoeopathic journal – Article on Eel or serum Anguillae Icthyotoxin by A.C.G Gross ; volume 68, Issue4, October 1979, pages 227-229 [3] Eel Wikipedia. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eel [4] Boericke William, M.D.; Boericke’s new manual of homoeopathic materia medica with repertory ; Third revised & augmented edition based on ninth edition; B. Jain Publishers (P) Ltd.
5 Sankaran, P; The Elements of Homoeopathy; edited by: Dr. Rajan Sankaran; Volume1; Reprint Edition 2016; homoeopathic medical publishers; ISBN-81-900810-3-9; Printed at Parksons Graphics Pvt.Ltd.
[6]Italian Journal of Zoology-Article on European eel: A History which must be rewritten; Castellato Sandra 69 321-324 (2002); ISSN: 1125-0003(print). [7] Verma P Encyclopedia of Homoeopathic Pharmacy. [8] Aida, K., Tsukamoto,K., Yamauchi,K. (Eds); Eel Biology with 209 figures, Including; Softcover Reprint of the Hardcover 1st Edition 2003; Springer- Velag Tokyo 2003. [9] R. J.Balment, Y. Takei; Article on Biochemistry and Physiology of a Family of Eel Natriuretic Peptides; July 1993; PMID: 24202475; DOI: 10.1007/BF00004565. [10]Boericke William, M.D.; Boericke’s new manual of homoeopathic materia medica with repertory ; Third revised & augmented edition based on ninth edition; B. Jain Publishers (P) Ltd. [11]British Homoeopathic journal – Article on Eel or serum Anguillae Icthyotoxin by A.C.G Gross ; volume 68, Issue4, October 1979, pages 227-229 [12] Sankaran, P; The Elements of Homoeopathy; edited by: Dr. Rajan Sankaran; Volume1; Reprint Edition 2016; homoeopathic medical publishers; ISBN-81-900810-3-9; Printed at Parksons Graphics Pvt.Ltd. [13] RADAR OPUS SOFTWARE [1] British Homoeopathic journal – Article on Eel or serum Anguillae Icthyotoxin by A.C.G Gross ; volume 68, Issue4, October 1979, pages 227-229 [1] British Homoeopathic journal – Article on Eel or serum Anguillae Icthyotoxin by A.C.G Gross ; volume 68, Issue4, October 1979, pages 227-229 [1] Eel Wikipedia. Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/EelREFERENCES:
[1] Boericke William, M.D.; Boericke’s new manual of homoeopathic materia medica with repertory ; Third revised & augmented edition based on ninth edition; B. Jain Publishers (P) Ltd.5 Sankaran, P; The Elements of Homoeopathy; edited by: Dr. Rajan Sankaran; Volume1; Reprint Edition 2016; homoeopathic medical publishers; ISBN-81-900810-3-9; Printed at Parksons Graphics Pvt.Ltd.
[1]Italian Journal of Zoology-Article on European eel: A History which must be rewritten; Castellato Sandra 69 321-324 (2002); ISSN: 1125-0003(print). [1] Verma P Encyclopedia of Homoeopathic Pharmacy. [1] Aida, K., Tsukamoto,K., Yamauchi,K. (Eds); Eel Biology with 209 figures, Including; Softcover Reprint of the Hardcover 1st Edition 2003; Springer- Velag Tokyo 2003. [1] R. J.Balment, Y. Takei; Article on Biochemistry and Physiology of a Family of Eel Natriuretic Peptides; July 1993; PMID: 24202475; DOI: 10.1007/BF00004565. [1]Boericke William, M.D.; Boericke’s new manual of homoeopathic materia medica with repertory ; Third revised & augmented edition based on ninth edition; B. Jain Publishers (P) Ltd. [1]British Homoeopathic journal – Article on Eel or serum Anguillae Icthyotoxin by A.C.G Gross ; volume 68, Issue4, October 1979, pages 227-229 [1] Sankaran, P; The Elements of Homoeopathy; edited by: Dr. Rajan Sankaran; Volume1; Reprint Edition 2016; homoeopathic medical publishers; ISBN-81-900810-3-9; Printed at Parksons Graphics Pvt.Ltd. [1] RADAR OPUS SOFTWAREAbout Author:
Dr Vinita Choudhary, PGT
R.B.T.S. Govt. Homoeopathic Medical
College and Hospital, Bihar





