Abstract: Glaucoma is a chronic slowly progressing disease that has a multifactorial pathology process that damages the eye from oxidative stress, free radicals and increased IOP and can damage further optic nerves. If damage continues it leads to permanent vision loss. There is a need of conventional treatment along with surgery in Glaucoma cases but these treatments carry adverse effects and lead to complications .But Homoeopathy can cure Glaucoma , its subjective and objective symptoms and prevents further complications .Damage by Glaucoma cannot be reversed but proper treatment helps prevent vision loss especially in the early stages of the disease.
Keywords– Glaucoma and Homoeopathy.
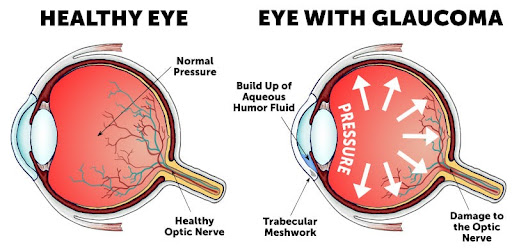
Introduction– Glaucoma is one of the chronic progressive disorders of the eye characterized by visual loss, mainly occurring due to a rise in the intraocular pressure. The most important factor which causes a rise in the intraocular pressure is obstruction in the drainage of the aqueous humor through the angle of anterior chamber and at the pupil.The intraocular pressure (IOP) refers to the pressure exerted by intraocular fluids on the coats of the eyeball. The normal IOP varies between 10 and 21 mm of Hg.
Open-angle Glaucoma-
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form of the disease. The drainage angle formed by the cornea and iris remains open, but the trabecular meshwork is partially blocked. This causes pressure in the eye to gradually increase. This pressure damages the optic nerve. It happens so slowly that you may lose vision before you’re even aware of a problem.
Angle-closure Glaucoma–
Angle-closure glaucoma, also called closed-angle glaucoma, occurs when the iris bulges forward to narrow or block the drainage angle formed by the cornea and iris. As a result, fluid can’t circulate through the eye and the pressure increases. Some people have narrow drainage angles, putting them at increased risk of angle-closure glaucoma.
Normal-tension glaucoma-In normal-tension glaucoma, the optic nerve is damaged even though eye pressure is within the normal range.
Glaucoma in children-
It is possible for infants and children to have glaucoma. It may be present from birth or developed in the first few years of life. The optic nerve damage may be caused by drainage blockages or an underlying medical condition.
Pigmentary glaucoma–
In pigmentary glaucoma, pigment granules from the iris build up in the drainage channels, slowing or blocking fluid exciting the eye.
General Management-
- Measuring Intraocular pressure is called Tonometry.
- Testing for optic nerve damage with a dilated eye examination and imaging Test.Optical Coherence Tomography.
- Checking the areas of vision loss, also known as visual field test. Projection Perimetry
- Measuring corneal thickness is called as pachymetry.
- Inspect the drainage angle called as Gonioscopy.
- Glaucoma is treated by lowering intraocular pressure, including treatment like eye drops, oral medicines, laser treatment or surgery.
Role of Homoeopathy-
- Aconite – Pain extending down the face, after exposure to cold winds, eyeball feel as if it would be forced out of the orbit<by motion or touch, intense photophobia, pupils contracted only at the beginning.
- Comocladia Dentata– Glaucoma, sense of fullness; eyeball feels too large. Motion of eyes aggravates. Ciliary neuralgia with eyes feeling large and protruded, especially right. Worse, near a warm stove; feels as if pressed outward. Sees only glimmer of light with left eye
- Phosphorous– Glaucoma, Thrombosis of retinal vessels and degenerative changes in retinal cells. Degenerative changes where soreness and curved lines are seen in old people. Retinal trouble with lights and hallucination of vision. Black points seem to float before the eyes. Patient sees better by shading eyes with hand. Fatigue of eyes and head even without much use of eyes.
- Cedron – Shooting over the left eye. Severe pain in the eyeball, with radiating pains around the eye, shooting into the nose. Scalding lachrymation. Supra-orbital neuralgia periodic. Iritis, choroiditis.
- Physostigma – Vision dim; from blur or film; objects mixed. Pain after using eyes; floating black spots, flashes of light, twitching.
- Osmium – Glaucoma; with iridescent vision. Violent supra and infra-orbital neuralgia; violent pains and lachrymation. Green colors surround candle-light. Conjunctivitis. Increase in intraocular tension, dim sight.
- Belladonna – Throbbing deep in eyes while lying down. Pupils dilated . Eyes feel swollen and protruding, staring, brilliant; conjunctiva red; dry, burn; photophobia; shooting in eyes. Ocular illusions; fiery appearance. Diplopia, squinting, spasms of lids. Sensation as if eyes were half closed.
- Spigelia Anthelmia – Feel too large, pressive pain on turning them. Pupils dilated; photophobia; rheumatic ophthalmia. Severe pain in and around the eyes, extending deep into the socket. Ciliary neuralgia, a true neuritis.
- Gelsemium– Choroidal and venous congestion, either with or without serous effusion. Amaurotic symptoms, with dilatation of pupils, disturbed accommodation, pain in eyes, with or without accommodation.
- Hamamelis– Venous congestion, Haemorrhoids, conjunctival vascularity ,ciliary neuralgia, photophobia, lachrymation.
- Kali Iod– Incipient glaucoma in syphilitic subjects, dull and discolored state of iris, burning in iris, lachrymation, dilated pupils, Amaurotic symptoms.
- Nux Vomica– Marked morning aggravation, atrophy of optic nerve.
Conclusion
Homoeopathic medicines are liable to control IOP, to prevent Visual blindness, to maintain the optical status, and functional condition of Glaucomatous structure, reduce the objective and subjective distress, and prevent complication after Glaucoma is diagnosed.
References
- SihotaRamanjit, Tondon Radhika; Parson’s diseases of eyes; 21st edition; 2011; Elsevier indiaPvt Ltd.
- https://www.homeobook.com/homoeopathy-and-glaucoma/
- Boericke William. Pocket manual of homoeopathic Materia Medica and repertory; Student edition 2012; B. Jain Publisher, New Delhi
- Allen.H.C. keynotes rearranged and classified with leading remedies of Materia Medica and bowel nosodes; Student edition 2011; B. Jain Publisher, New Delhi.
- B.M Chatterjee; Handbook of Ophthalmology;6th Edition, CBS Publishers and Distributors Pvt Limited.
- Samuel Lilienthal, Homoeopathic Therapeutics The classical Therapeutics Hints,28th Impression, B Jain Publishers Pvt Limited.